Singapore Airlines Case Study
Jan 28,22Singapore Airlines Case Study
Question:
Singapore Airlines Case Study
Singapore Airlines was created in 1972 following a separation from Malaysian Airlines. In the wake of reorganization, Singapore Airlines undertook aggressive growth, investing and trading to maximize profitability and expand market share. Through this change, a new company philosophy emerged, “Success or failure is largely dictated by the quality of service it provides” (Wyckoff, 1989). By reinventing the company infrastructure and introducing new initiatives focused on excellence in customer service, Singapore Airlines became a global leader in the service industry, elevating existing standards among competitors.
Evaluation of Workforce Management Program
The strategy widely utilized by Singapore Airlines to ensure differentiation in an increasingly competitive market was its attention to in-flight service. “Good flight service [was] important in its own right and is a reflection of attention to detail throughout the airline” (Wyckoff, 1989). This statement perpetuated the belief that excellence in service was directly tied to the careful selection and individual performance of in-flight crews charged with the responsibility of fulfilling the needs of individual passengers and exuding the levels of service demanded by the organization. Applicants destined to work as flight stewards were drawn from a very young population, typically spanning the ages of 18-25 years of age with high school equivalency against the English system of education. Selection of applications was competitive largely due to the degree of skill, poise, and experience required of its candidates. These policies led to the on-boarding of a highly skilled and youthful workforce with positive attitudes and a willingness to be trained. Critique of this approach revealed several disadvantages. The most significant being the potential for greater turnover when hiring a younger population as opposed to an older, more experienced crew. Experience alone would play some role in the development of new employees, as greater experience would bring greater poise and confidence. However, in light of the predominant population Singapore Airlines catered to, a younger in-flight crew would remedy the awkwardness likely to be encountered by older clients being served by older crew members. In addition, a younger crew would likely be more accepting of new procedures and less cynical of the requirements of employment.
Answer:
Introduction
Student name:
Student ID:
Module number:
Abstract
In the relevant assessment the workforce management operations and strategies have been discussed. Based on the relevant case study the SWOT and pastel analysis has been done regarding Singapore Airline industry
Table of Contents
Introduction. 3
Background. 3
PESTLE analysis. 3
Porter’s five forces analysis. 4
Strategic Capabilities and SWOT analysis. 5
Porter’s strategies. 6
Challenges. 7
Conclusion. 7
Reference list 8
Introduction
Singapore Airlines is one of the busiest airline industries with massive domestic and international operations to transport passengers. In this relevant assessment, the influential operational tools and market position of the Singapore airline industry will be analysed. The potential growth and sustainable factors regarding the relevant industry will be explained.
Background
In 1972 the Singapore Airline was invented as a chain network of Malaysian airlines. In today’s competitive era Singapore Airlines has become one of the most valuable international leaders in the global airline industry. Though there is a massive hazardous situation that has been observed during the transportation operation of Singapore Airlines. The recruitment process and operation of Singapore airlines needs to be modified with more critical actions. The recruitment process should be tougher for the young or newly joining crew members.
PESTLE analysis
| Political | Economic | Socio-cultural | Technological | Environmental | Legal factors |
| Government support has been achieved by the Singapore Airline industry. | Economic support from the country government. | Influential attitudes by the crew members of airline industries. | Innovative technological tools and components in planes. | Sustainable operations by Singapore airline industries developed its operations. | Global support to run operation in the international market. |
Political factors: It has been seen that due to the global support by the political parties and the worldwide organisation the Singapore Airline industry got the opportunity to grow its profit.
Economic factors: Global economic investment ts and supports have been identified.
Socio-cultural factors: The global airline industries have supported the relevant industry to run the airline transportation operations.
Technological factors: Innovative technology has been adopted by the industry that helped to compete with rival airline industries.
Environmental factors: Thais industry achieved global support due to the most attractive tour places and locations. The marketing strategies indicate to energise the industrial operation with more critical tools (Visnjic, Neely & Jovanovic, 2018).
Legal factors: Through its operational period since its establishment date it only focused on increasing the quality of the services to the passengers.
Porter’s five forces analysis
Threat new entrants: Due to the internal problems in the Singapore airline industries regarding the recruitment process other competitors can highly compete in this current industry.
Bargaining power of buyers: The bargaining power of buyers or clients of the Singapore Airline industry is high. In today’s competitive era industries focus on commercial investment in their operations (Eastmure, Cummins & Sparks, 2020).
Threats of substitutes: There are high market threats by the other East-Asian airline industries to Singapore airlines. It should focus on resolving its internal complexities with the crew members. Good flight services need to be provided by the members of the Singapore airline industry.
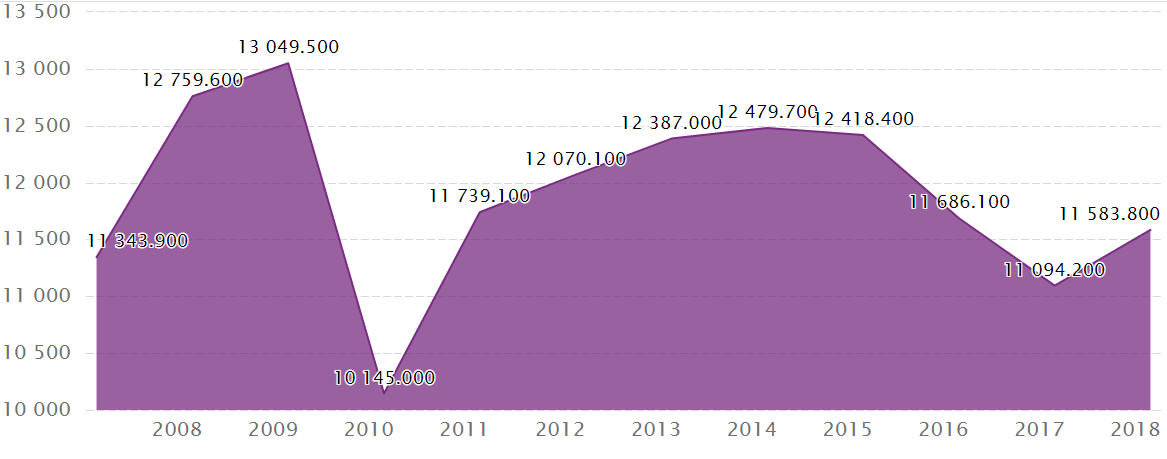
Figure 1: Financial growth and development of Singapore airline industry in last few years
Source: (Ceicdata, 2022)
Rivalry among existing competitors: The rivalry among the existing airline industries specifically in the south-East Asian airline is high. Thus, the relevant industry should critically regulate its operations with more useful actions.
The bargaining of suppliers: The suppliers of Singapore airline industries are the airline vehicle manufacturers and their bargaining poachers are quite high. Thus, it is important to increase the economical sources of the Singapore airline industry to afford better quality airline vehicles and well-structured tools in the internal premises of the plane.
Strategic Capabilities and SWOT analysis
| Strength | Threat |
| ● High demand by global consumers
● The most needed flight industry |
● High market competition
● Growth of other companies in the industry in East-Asian region |
| Weaknesses | Opportunity |
| ● Poor quality flight services
● Untrained hostages |
● Increasing economical sources
● Developed operational cost |
Strength: The strength of the Singapore airline industry indicates its high demand among its stakeholders. As it is known that Singapore is a famous tourist destination, the relevant industry has high demand from passengers and global tourists.
Opportunity: Singapore is one of the busiest business destinations for global industries. So, it is an opportunity ahead of the Singapore Airlines industry to utilise it for better improvement.
Weakness: It has been identified from the provided case study that Singapore Airlines is facing an issue with its post-flight services. Due to less effective flight services airline industries can get inappropriate financial loss (Prissia, & Daryanto, 2019). Misunderstanding among the passengers and crew members has been observed.
Threat: There is a high threat towards the Singapore airline industry from its existing competitors. High market threats can reduce the level of global investments from external investors.
Porter’s strategies
Cost leadership: Making the tickets cheapest is the strategy that can be applied by the Singapore airline industry. After the pandemic situation, many tourists have lost their capacity to afford the travelling cost. Through utilising this strategy the Singapore airline industry can increase its profit.
Focus: The main focus of Singapore airline industries should be on increasing their flight service quality. Through providing proper training to its crew members it is possible to boost their efficiencies. Providing proper care to the old aged passengers is one of the main duties of Singapore airline employees.
Differentiation: Singapore airline industry differently chosen the strategy to provide influential services to its passengers. Through providing and teaching the youth crew members it improved their motives and mindset. These actions specifically impacted their service quality.
Strategic choice of Singapore Airlines: With the support and direction of the Singapore Airlines CEO Mr. Goh Choon Pong has gathered massive sauces. The Singapore airline industry needs to apply the strategic pricing method regarding its services and transportation cost. After the recent pandemic situation, its economical sources had been sealed by the relevant industry.
Challenges
Reduced economical source and poor employee performances: In order to develop the economical sources Singapore airline industry needs to improve its services. Implementation of innovative tattoos and flexible components into the flight premises is required. An enhanced market strategy is required to avoid market-related threats (Kleber, Neto & Reimann, 2020). Thus, the Singapore flight industry needs to improve its economical sources. There are the challenges regarding the reduced financial investment that has become one of the greatest threats to the Singapore industry.
Conclusion
After analysing the entire assessment it can be concluded that due to the high market competition Singapore airline industry needs to develop flight services more critically. It has been explored through providing proper training to the flight hostages as crew members it is possible to boost the flight services. The existing market threats can be avoided if Singapore airline is capable of boosting its transportation operations by making the passengers satisfied.
Reference list
Ceicdata. (2022). Singapore Airlines: Revenue | Economic Indicators | CEIC. Ceicdata.com. Retrieved 21 January 2022, from https://www.ceicdata.com/en/singapore/singapore-airlines-statistics/singapore-airlines-revenue.
Eastmure, E., Cummins, S., & Sparks, L. (2020). Non-market strategy as a framework for exploring commercial involvement in health policy: a primer. Social Science & Medicine, 262, 113257. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.113257
Kleber, R., Neto, J. Q. F., & Reimann, M. (2020). Proprietary parts as a secondary market strategy. European Journal of Operational Research, 283(3), 929-941. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2019.11.062
Prissia, D., & Daryanto, W. M. (2019). Financial Performance Analysis and Evaluation of Airline Industry Indonesia: Case Study of PT Garuda Indonesia to Support Vision 2020″ Beyond The Sky” for the Period of 2014-2018. International Journal of Business, Economics and Law, 20(1), 10-21. Retrieved from: http://ijbel.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/IJBEL20_30.pdf
Visnjic, I., Neely, A., & Jovanovic, M. (2018). The path to outcome delivery: Interplay of service market strategy and open business models. Technovation, 72, 46-59. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2018.02.003





