Malaysian Derivative Market
Feb 1,22Malaysian Derivative Market
Question:
Discuss about the Malaysian Derivative Market.
Answer:
Introduction
Student name:
Student ID:
Module name:
Table of Contents
Introduction. 3
Discussion. 3
Conclusion. 6
Reference list 7
Introduction
A derivatives market mainly indicates a financial market that provides various kinds of financial instruments and accessories, for example, future contracts and many more. Various options that are related to the value of underlying assets can also be considered as an essential instrument of derivatives markets. Four types of participants are available in a derivative market. They are the hedgers, the speculators, the arbitrageurs and the margin traders. In order to prepare the contract, the market uses four main derivatives. They are the options, the futures, the forwards and the swaps. Similarly, the derivative market of Malaysia is a subsidiary market of Bursa Malaysia. The market was established in 1993. The market provides various kinds of operational activities and it maintains various kinds of equity, rate of interest, bonds, agricultural commodities like palm oil, crude palm oil, palm kernels and many more. It includes various kinds of metal commodities like gold, tin and others in order to grab the future markets and various optional markets for trading as well as other optional services. The products can get easily on the platforms of the CME Globex electronic trading. It helps the authority of Malaysia to distribute the products along with the special offerings greatly to the global market. The operational activities of the market are going to be discussed here briefly.
Discussion
Various financial derivatives are one of the most essential elements of the Malaysian derivatives market. The products of the financial derivative market mainly indicate various short term interest rates. For example, Kuala Lumpur Interbank offers short term interest rates for three months only (Vo, Huynh & Ha, 2019). In order to do that, the bank uses the ringgit time deposit scheme for the wholesale market. The maturity period of the scheme is three months where the year is considered for 360 days. The size of the contract is RM 1000000 and the contractual months are considered quarterly according to the scheme. It can be placed in March, June, the month of September and the month of December. The scheme can be continued for up to five years continuously. In order to activate the scheme, the trading time of the bank is Monday to Friday from 9.00 am to 12.30 pm and then from 2.30 pm to 5.00 pm. The final settlement value of the scheme can be calculated as 100.00 ringgit minus the 3 months KLIBOR according to the report of Reuters Limited. In the event, the calculation stated above, can not be created.
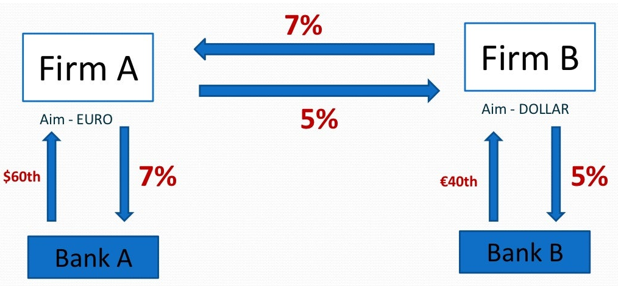
Figure 1: The image of currency swap for financial derivative
Source: (Afrina et al., 2020)
The value of the final statement can be created as 100.00 ringgit minus the 3 months LIBOR. Not only can that but the value of the final settlement be determined by the rate of exchange. However, the financial derivatives can support long term future contracts also. The scheme of five-year securities from the government of Malaysia can be created for future contracts as a financial derivative. Here, the main instrument is the securities of the Malaysian government. The maturity period of these securities is five years. The rate of the coupon is six per cent per annum that is payable by the semi-annual mode (Afrina et al., 2020). The principal value of the contract is RM 100000.00 that is for five years. The scheme can consider four-quarter months, for example, March, June, the month of September and the month of December in every fiscal year.
However, the derivative market of Malaysia can offer various kinds of commodity derivatives also. The gold future (FGLD) is one of the most reliable ways to buy and sell gold and various gold products in Malaysia (Chong, 2021). The gold future is a ringgit denominated contract that is traded in the Malaysian derivatives market. The contract of gold futures exposes the movement of the gold price in the international market. The contract size of the scheme is 100 grams and three successful months can be spotted up to twelve months. The trading hour is Monday to Friday from 9.00 am to 12.30 pm in the morning session. It can be continued from 2.30 pm to 7.00 pm in the afternoon session according to the Malaysian timetable. The pricing unit is Malaysian ringgit (MYR) here. A fluctuation of minimum price is considered MYR 0.5 per gram of gold. Cash settlement is the final settlement here. the gold future has many advantages. It can attract global access. As the gold products can be traded electronically on various CME GLOBEX platforms it allows individuals as well as commercial traders to trade the gold anywhere across the whole world very easily. Another great advantage of this kind of trade is the scheme provides regulated trading. It is very much secure and highly confidential (KÜÇÜKÇOLAK, YILMAZ & AYYILDIZ, 2020). The marketplace is transparent for these kinds of trade. In order to make it more effective, the security commission of Malaysia is involved here. They regulate the trade continuously and very effectively.
Figure 2: The image of gold future derivative
Source: (KÜÇÜKÇOLAK, YILMAZ & AYYILDIZ, 2020)
Another derivative is the equity derivative that can be found in the derivative market of Malaysia. The Bursa Malaysia Kuala Lumpur Composite Index (FBM KLCI) is an equity derivative in the Malaysian market that provides composite index futures contracts (Azrak & Foziah, 2020). The contracts mainly help to expose the underlying constituents of FBM KLCI. The instrument is actively used by various kinds of large institutions. However, various retail investors and traders can also use these instruments for their portfolios. Here, the contract size can be multiplied by MYR fifty and the cash settlement can be used for considering the value of the final settlement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it can be said that the derivative market of Malaysia is one of the great places for the investors and the traders of the country. It helps the investors in expanding their businesses in many ways. Mainly there are three types of derivatives are available, for example, commodity derivatives, equity derivatives as well as financial derivatives. The entire derivative has their advantages and regulations. That is the reason all the derivatives are discussed here briefly.
Reference list
Afrina, T., Beg, T. H., Zayed, N. M., Hossain, M. S., & Shahi, S. K. (2020). An analysis of the effects of coronavirus (COVID-19) on the international financial derivatives market, 2020. Indian Journal of Finance and Banking, 4(2), 93-98. DOI: https://doi.org/10.46281/ijfb.v4i2.757
Azrak, T., & Foziah, H. (2020). Islamic embedded options in structured products of Malaysia: issues and challenges. İslam Ekonomisi ve Finansı Dergisi (İEFD), 6(1), 107-129. Retrieved from: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/jief/issue/55732/677957
Chong, J. Y. (2021). The Emerging Asia Pacific Capital Markets: Malaysia. CFA Institute Research Foundation Briefs. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3807401
KÜÇÜKÇOLAK, N. İ., YILMAZ, M. K., & AYYILDIZ, E. M. (2020). Gold spot and derivatives markets interaction in Turkish financial markets. İstanbul Ticaret Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi, 19(Temmuz 2020 (Özel Ek)), 295-309. Retrieved from: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/iticusbe/issue/56181/763237
Vo, D. H., Huynh, S. V., & Ha, D. T. T. (2019). The importance of the financial derivatives markets to economic development in the world’s four major economies. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 12(1), 35. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm12010035





