Financial Performance Of EasyJet Plc Vs Flybe Group Plc
Mar 11,22Financial Performance Of EasyJet Plc Vs Flybe Group Plc
Question:
Discuss about the Financial Performance of EasyJet Plc Vs Flybe Group Plc.
Answer:
Financial Performance of EasyJet Plc Vs Flybe Group Plc
Student Name:
Student Id:
Module Name:
Executive Summary
The content demonstrates the in-depth and comparative discussion about the financial performance of EasyJet Plc v/s Flybe Group Plc. In addition to the detailed information of revenue generation, profitability rate, liquidity rate, this also entails the strong competitors of the respective companies in the market. Both of the companies follow cost-cutting strategies to survive in the ever-changing market of the aviation industry. The recent blow of pandemic has impacted the decreased growth rate and turnover of the companies. The strategies are innovative to gain a competitive advantage in the industry and the detailed discussion help all the stakeholders, market researchers to have an overview of the ongoing trends in the companies’ business operations and execution.
The factors of globalization and the combined efforts of government, market, competitive consideration and the government influence the performance. Both of the companies try to reach the client through their easy availability of the service. The most common strategies to be implemented are differentiation and cost management strategy to survive in the global market. It is crucial to opera in an airport that creates higher revenue. The focus is to enhance the GDP and tap the latent requirements of the diverse population most of the middle class.
Table of Contents
Introduction. 4
Discussion. 4
Conclusion. 9
References. 10
Introduction
The companies like EasyJet and Flybe enter the airline industry in spite of the shard rivalries and patent economic forces existing in the sector. The attractiveness and competitiveness of the market are enhanced by the factor of internalization. The clear perception makes the discussion of thy financial performance much easier and more receptive.
Discussion
The second-largest company of airline in the UK is EasyJet operating 241 aircraft on 735 routs. Besides extending to the passengers affordable service for long distances, it also gains its name for creating various graphic designs. The financial performance of the company can be discussed by taking into account the point below:
Easy Jet: Financial analysis
Easyjet demographically divided the turnover between Non -UK and the UK resulting in the depreciation of the aircraft and other maintenance costs. The aircraft value is transformed to a residual value between $12 and 20 million. As for the leased aircraft, maintenance cost is mandatory, it might vary highly and be estimated to the best knowledge of the management. Impairment tests are held yearly to have a better understanding of the economical situation. The company’s economic position weights the perception by the financial market. This is a low-cost airline that functions from 14 bases throughout Europe. Performance in the area of Return on Capital is 6% lower than other companies. The asset utilization b the company is more effective than Flybee (ANDREAS-DANIEL, 2019). Risk management and liquidity ratio are very good as consecrated by Flybe. The moderate performance of the company results in less return on equity. The profitability of the company is highly affected due to the pandemic-induced market of the UK. Due to the same reason, the trade growth is compromised and persistent policies are applied to overcome the challenges and continuous improvement.
Rivals in market
Easyjet operates within the tough market that is constantly being powerful by the consumer’s variable demands. With the amenities of low-cost flights and first com, the first-served practice has drawn in a large pool of international client5s. The mobile apps and various commercial channels are utilised for lad generation which results in profitability and revenue generation.
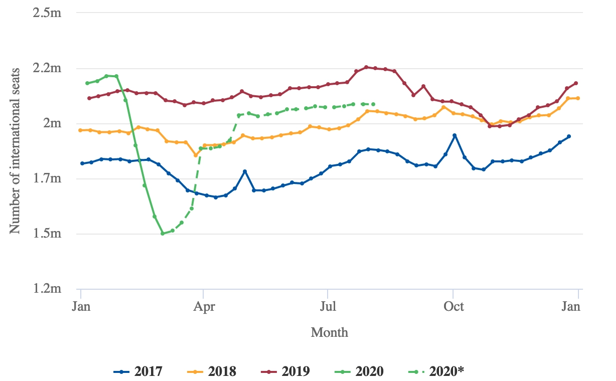
Figure 1: Market Analysis of Easy jet
Source: (ANDREAS-DANIEL, 2019)
Value driver analysis
24% of consumers recently use online boarding passes and they have facilitated the control of airport inflation including take-off fees and favourable landing. Hedging for $519 /tonne, EasyJet protect itself from price fluctuations in the volatile aviation fuel market. The shareholders consented to variations so that the airline is controlled and EU-owned after Brexit. Revenue comes from the airline’s enhanced supply capacity. The company attains substantial revenue growth through the corporate strategy of cost-efficiency. EasyJet accommodated more than 80 million passengers in 86 million seats increasing the load factor by 90%. Total revenue generated by the business was above more than 5 billion. The policy of the high load factor contributes to the network economy. However, the model can be referred to as the low cost despite the ancillary revenues. With the recent happening of falling unemployment and increased GDP of a country like Spain, there is a stimulus in demand for Easyjet in a highly cost-sensitive industry.
Flybe: Market and competitors
Flybe influences the shareholder’s decision and overall Europan economic development by branding itself as the largest regional aviation operator having almost 96% of group turnover. Its strong rivals in the market that operate at low-cost are Easyjet and Ryanair. The challenge of the new competitors has pushed the company to adopt a few changes. Flybe has been introduced itself as a regional airline of low expenditure based on no-frills models. The Company has its focus on the UK market and the installed models leverage regional airports in the country. As opposed to the Esayets strategy based on the price, the market strategy of Flybe is formed upon convenience (Waltenberger & Ruff-Stahl, 2018). The organisational strategy involves a particular segment of the market and making way for the nearest airport affordably. Rebranding of the company occurred in 2002 transforming its name from Jersey European Airways. The strategies of the company cater to a large number of UK airports.
Financial Analysis
Flybe liquidity is lower than EasyJet and the company can’t transform its asset into cash as fast as EasyJet.This is a major issue consolidating the crisis in the market and the last financial year although liquidity has increased by 4%.it was spotted to be critical. However, Flybe has improved the gearing ratio that puts it in the same line as EasyJet and other competitors (Barrows, 2019). In order to develop the performance, Flybe initiated a fuel surcharge of $3.00 per person. However, the ownership cost involving insurance, maintenance, other expenses have been increased. There also has been a sharp rise in control provider or route charge. The increase has been on account of the augmented partner or supplier rate and movements of the exchange rate. Despite the turbulent market, the company has enhanced revenue year by year. Efficient performance is in the market fasciitis the smooth revenue generation. Facing strong rivals and mounting expenditure, a drastic decline takes place regarding operating profit. The company has gathered a loss of 4.3 million that the company still struggles to overcome.
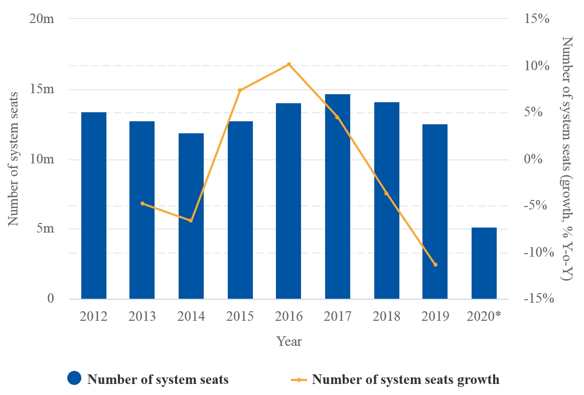
Figure 2: Flybe Financial Analysis
Source: (Barrows, 2019)
Value driver analysis
The value-driving mechanisms influence the business of Exeter-based airline companies. This will help to analyse and compare the performance of the company in contrast with the existing competitors in the market (Tunahan & ÇINAROĞLU, 2018).In the airline industry, the load factor is very much important and this is the proportion between seat com available and seat-com used. In the first half;f of last year, the ratio face the deadline from 63.32% to 60.97% yet remain stable last year. The highest yield maintained by Flybe is noticeable. In terms of the average cost per kilometre, the growth is intense and almost double compared with EasyJet (Stanojević, Mitić & Radivojević, 2022). Although the company has its basis on the cost-cutting strategy, the business model can not be called the low-cost one. During the market turbulence and the pandemic crisis, it becomes risky to maintain the structure.
Conclusion
The current trends in the UK domestic market lead to the company like EasyJet and Flybe scaling own their domestic routes within the UK. It becomes a challenge for the airline operators to export the model outside of the UK. The financial analysis suggests the total refurbishment including renewing the fleet and staff reduction.
References
ANDREAS-DANIEL, C. O. C. I. Ș. (2021). DETERMINING THE PLACE IN THE RANKING BASED ON THE FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF THE MOST POPULAR AIRLINES IN EUROPE. Annals of’Constantin Brancusi’University of Targu-Jiu. Economy Series, (2). Retrieved from: https://www.utgjiu.ro/revista/ec/pdf/2021-02/13_Cocis.pdf
Barrows, S. D. (2019). Assessing the stock market performances of Eu low-cost airlines. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 9(4), 95. Retrieved from: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Samuel-Barrows/publication/334270412_Assessing_the_Stock_Market_Performances_of_EU_Low-Cost_Airlines/links/5d
Stanojević, J., Mitić, G., & Radivojević, V. (2022). ECONOMIC IMPACT OF COVID-19 ON THE EUROPEAN AIRLINE INDUSTRY. TEME, 1181-1195. Retrieved from: https://biopen.bi.no/bi-xmlui/bitstream/handle/11250/2825243/2940864.pdf?sequence=1
Tunahan, A. V. C. I., & ÇINAROĞLU, E. (2018). AHP TEMELLİ TOPSIS YAKLAŞIMI İLE HAVAYOLU İŞLETMELERİNİN FİNANSAL PERFORMANS DEĞERLEMESİ. Cumhuriyet Üniversitesi İktisadi ve İdari Bilimler Dergisi, 19(1), 316-335. Retrieved from: http://esjournal.cumhuriyet.edu.tr/en/download/article-file/481441
Waltenberger, J., & Ruff-Stahl, H. J. K. (2018). Implications of short scheduled ground times for European carriers. International Journal of Aviation, Aeronautics, and Aerospace, 5(3), 8.. Implications of short scheduled ground times for European carriers. International Journal of Aviation, Aeronautics, and Aerospace, 5(3), 8. Retrieved from: https://commons.erau.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1244&context=ijaaa





