Master the Rules of Compound and Complex Sentences (With Examples)
Apr 29,22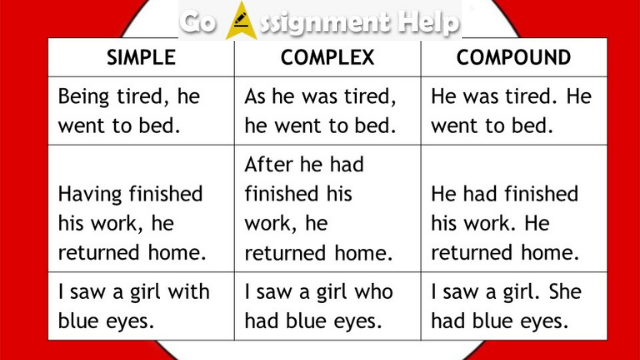
Sentence structure is one of the most important aspects of writing. Good sentence structure makes your writing clear and easy to read. Bad sentence structure can make your writing confusing and difficult to understand.
There are three main types of sentences: simple, compound, and complex. Each type has its own rules about how the parts of the sentence must be arranged:
- Simple sentences are the most basic type of sentence. They consist only of a subject and a verb, and they express a complete idea. For example, “The cat is sleeping.” Simple sentences can be short or long, but they should always be clear and easy to understand.
- Compound sentences are two simple sentences joined together by a conjunction. For example, “The cat is sleeping and the dog is barking.” The two simple sentences must be related to each other in some way – they can’t just be two random thoughts stuck together.
- Complex sentences are made up of one main clause and one or more subordinate clauses. A subordinate clause is a group of words that contains a subject and verb, but it can’t stand on its own as a simple sentence. For example, “Because the cat was sleeping, I decided not to disturb him.” This sentence consists of one main clause (“I decided not to disturb the cat”) and two subordinate clauses (“because the cat was sleeping” and “the cat was sleeping”).
Compound and complex sentences are more interesting and nuanced than simple sentences. They can express multiple ideas, and they can make your writing more sophisticated. However, they can also be more difficult to construct. This guide will teach you everything you need to know about compound and complex sentences so that you can use them effectively in your own writing.
When should you write a Compound Sentence?

There are several situations in which it can be useful to write a compound sentence, such as:
- If you want to express two closely related ideas, a compound sentence may be the best choice. For example, if you are describing the actions of two different characters in a story, or two different events that occur at the same time, then you will likely want to use a compound sentence.
- If you want to introduce variety into your writing, then adding a compound sentence can help make your writing less repetitive and predictable. For example, if you are describing the same event from multiple perspectives, or using different examples to illustrate a single idea, then a compound sentence may be helpful.
- If you want to emphasize the similarity or contrast between two ideas, then using a compound sentence can be an effective way to do so. For example, if you want to compare and contrast two different characters in a story, or two different aspects of a single event, then using a compound sentence can help you highlight those similarities and differences.
Rules to follow while writing Compound Sentences
Now that you know when to use a compound sentence, let’s take a look at the rules you need to follow to write one correctly:
- Use a conjunction to join the two simple sentences.
The most common conjunctions are “and”, “but”, “or”, and “so”. For example, “I wanted to go hiking, but it started raining.”
- Make sure that the two simple sentences you are joining together express closely related ideas.
For example, “I wanted to go hiking” and “it started raining” are both about my plans for a hiking trip. They are related because if it had not rained, I might have gone hiking.
- Ensure that the two simple sentences you are joining together have a similar structure and grammatical form.
For example, if the first sentence is in the present tense, then you should use a present-tense verb for the second sentence as well. Similarly, if one sentence uses an infinitive verb (“to go”) then the other sentence should also use an infinitive verb.
- Avoid using compound sentences for very short simple sentences, as this can make your writing sound choppy and jerky.
For example, it is generally best to avoid joining together two one-word sentences such as “The cat sat” and “The dog barked.” If you want to use a compound sentence in this case, it is usually best to add a few words to one or both of the simple sentences, to make them longer and more grammatically complex.
Examples of Compound Sentences
Now that you know how to write a compound sentence, let’s take a look at some examples of this writing structure in action:
- “We went skiing on Saturday and snowboarding on Sunday.” Here, two simple sentences are joined using the conjunction “and.” They express similar ideas (“skiing” and “snowboarding”) that occurred in close succession.
- “I love to hike, but I hate to camp.” Here, two simple sentences are joined using the conjunction “but.” They describe opposing ideas (“hike” vs. “camp”) that are closely related to one another.
- “The sun was shining brightly, so we decided to go to the beach.” Here, two simple sentences with similar structures (“The sun was shining” vs. “we decided”) are joined using the conjunction “so.” They express ideas that are directly related (“we went to the beach because the sun was shining”).
- “I wanted to go hiking, but it started raining.” Here, two simple sentences with similar structures (“I wanted” vs. “it started”) are joined using the conjunction “but.” They express ideas that are inversely related (“I didn’t go hiking because it started raining”).
- “The cat slept in the sun, and the dog barked at a squirrel.” Here, two simple sentences with different structures (“The cat slept” vs. “the dog barked”) are joined using the conjunction “and.” They express ideas that are related because they are both happening at the same time.
In these examples, you can see how the use of a compound sentence can help to express two related ideas more effectively than two simple sentences.
When should you write a Complex Sentence?

There are several situations in which it can be useful to write a complex sentence, including:
- If you want to express a single idea but use multiple supporting details. For example, if you have an argument that requires a lot of evidence and examples, then using complex sentences can help you organize your ideas effectively.
- If you want to express multiple things but have a single main idea. For example, if you want to describe the actions of multiple characters in a story or multiple events that occur one after the other, then you will likely want to use a complex sentence.
- If you want to emphasize the relationship between two ideas. For example, if you are discussing two concepts that are related in some way, such as a cause and effect relationship, then using complex sentences can help highlight those relationships.
Rules to follow while writing Complex Sentences
Now that you know when to use a complex sentence, let’s take a look at the rules you need to follow to write one correctly:
- Use subordinate conjunction to join the two simple sentences.
The most common subordinate conjunctions are “after”, “although”, “because”, “before”, “however”, “if”, “since”, “that”, “though”, “until”, “when”, and “while”. For example, “I will go to party after finishing my homework.”
- Make sure that the two simple sentences you are joining together express closely related ideas.
For example, “I will go to the party” and “after finishing my homework” are both about going out with friends after I finish my work. They are related because I am going to the party to relax and unwind after a long day of studying.
- Ensure that the two simple sentences you are joining together have a similar structure, grammatical form, and length.
For example, if one sentence uses the future tense (“I will go to the party”) then the other sentence should also use the future tense. And if one sentence is short and to the point, then the other sentence should also be short and to the point (“after finishing my homework”).
- Avoid using complex sentences for very short simple sentences, as this can make your writing sound choppy and jerky.
For example, it is generally best to avoid joining together two three-word sentences such as “The cat sat” and “the sky is blue.” If you want to use a complex sentence in this case, it is usually best to add a few words to one or both of the simple sentences, to make them longer and more grammatically complex.
Examples of Complex Sentences
Here are a few examples of complex sentences, to give you a better understanding of how they are constructed:
- Although I am failing math, I still get good grades in other subjects. Here, the subordinate conjunction “although” is used to join together two simple sentences (“I am failing math” and “I still get good grades in other subjects”). The first sentence expresses a negative idea, while the second sentence expresses a positive idea.
- We went out for dinner after we saw the movie. In this example, the subordinate conjunction “after” is used to join together two simple sentences (“We went out for dinner” and “We saw the movie”). The first sentence describes an event that happened first, while the second sentence describes an event that happened afterwards.
- I didn’t go to the party because I was too tired. Here, the subordinate conjunction “because” is used to join together two simple sentences (“I didn’t go to the party” and “I was too tired”). The first sentence expresses a negative idea, while the second sentence provides a reason or explanation for that negative idea.
- The sky is blue because the Earth’s atmosphere scatters sunlight in all directions. In this example, the subordinate conjunction “because” is used to join together two simple sentences (“The sky is blue” and “the Earth’s atmosphere scatters sunlight in all directions”). The first sentence describes a fact, while the second sentence provides an explanation of that fact.
- Though I have tried many times, I just can’t seem to pass this math test. Here, the subordinate conjunction “though” is used to join together two simple sentences (“I have tried many times” and “I just can’t seem to pass this math test”). The first sentence expresses an idea that contrasts with reality, while the second sentence provides a reason or explanation for that idea.
You may also check : PERSUASIVE WRITING TECHNIQUE
As you can see, complex sentences are fairly straightforward once you know the rules for using them. By following the four tips above, you can make sure that your complex sentences are both grammatically correct and express the ideas you want to communicate clearly.
As you can see, mastering the rules of compound and complex sentences takes time and practice. But with some effort and dedication and some help from GoAssignmentHelp experts, you can become a wizard at using them in no time!





0 responses on "Master the Rules of Compound and Complex Sentences (With Examples)"