A Guide to the Law of Conservation of Energy
Jan 20,20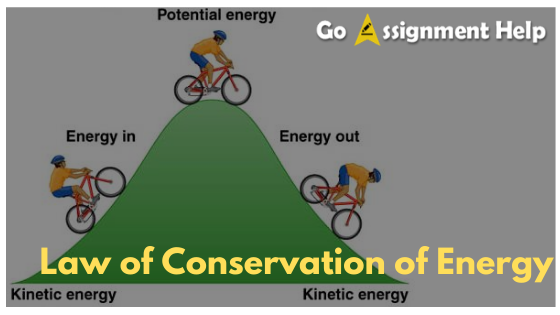
Definition of Law of Conservation of Energy:
The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. It keeps getting transformed from one form to another. Thus, the total energy in the universe remains constant.
The law of conservation of energy can be represented by a simple formula that is given below:
Total energy before a physical or a chemical change = Total energy after that physical or chemical change.
Examples of the law of conservation of energy:
- In a loudspeaker, electrical energy gets converted into sound energy.
- In a generator, mechanical energy gets converted into electrical energy.
Explanation of law of conservation of energy:
Environmentalists often speak of conserving energy or preventing it from getting lost. However, when environmentalists speak of saving energy, they mean to prevent the conversion of energy into non-usable forms.
In actuality, energy cannot be lost. It merely gets changed from one form to another within an isolated system. Here, the isolated system is the atmosphere. Thus, in the process of changing from one form to another, the total energy in the system remains conserved.
Verification of law of conservation of energy through a simple pendulum:
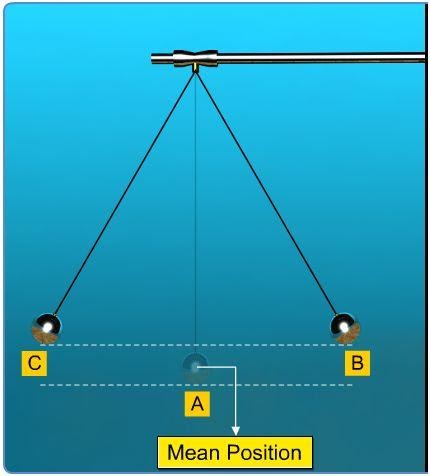
The law of conservation of energy can be explained or verified through a simple pendulum by demonstrating and explaining the conversion of potential energy into kinetic energy.
A simple pendulum is suspended freely from a stand, and its initial position is noted as A, which is also the reference point. The bob is now drawn to one side, say position B, and released. The bob goes from extreme position B to C, keeps oscillating, and eventually comes to rest at position A.
At positions B and C, the velocity of the bob is zero. Therefore, its kinetic energy is zero. Since the bob is at a height ‘h’ above its mean position, it poses potential energy at points B and C. At position A, the height of the bob from the reference point A is zero. Hence, the potential energy at point A is zero. The bob possesses kinetic energy only when it is at its mean position, while it possesses potential energy only when it is at extreme positions. At points between A-B and A-C, the bob possesses both kinetic energy and potential energy.
The total mechanical energy is the sum of the total potential energy and the total kinetic energy. Hence, the total mechanical energy at any point remains conserved. Thus, the law of conservation of energy is justified.
Another proof of the law of Conservation of Energy:
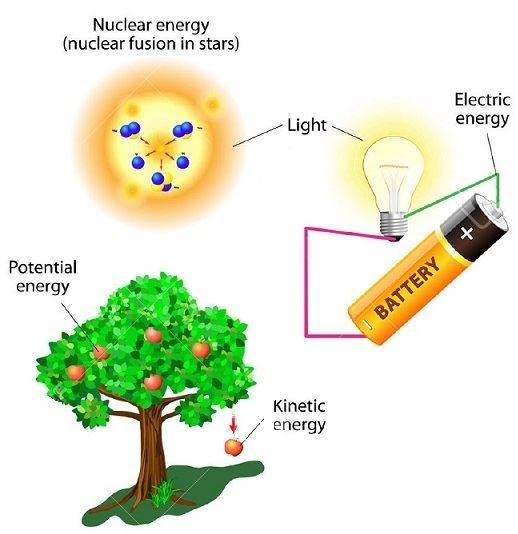
Let’s consider the potential energy at the surface of the earth to be zero. Again, let’s consider an example of a fruit falling from the tree.
When the fruit is on the tree, say point A, its velocity is zero. Thus, the kinetic energy is zero. Assuming the height of the fruit from the ground to be h, we get,
Potential energy = mgh
Thus, total energy at point A is mgh.
When the fruit is falling on the ground, potential energy is decreasing, and the kinetic energy is increasing. The fruit is falling freely under the influence of gravity. Let us assume that it is at a height x from the ground. Consider that point to be B.
Hence, at point B, total energy would be the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy.
Potential energy at B = mgx.
Now, using the third equation of motion, we get, v2=2g (h-x).
Putting the value of v2 in the formula of kinetic energy, we get,
Kinetic energy = 1/2m.2g(h-x) = mg(h-x)
Thus, Kinetic Energy at B is mgh-mgx
Total energy at point B is the sum of potential energy at B and kinetic energy at b, which is, (mgx + mgh – mgx), that is, mgh.
Thus, total energy at point B is mgh.
Let’s consider point C when the fruit hits the ground. At that point, potential energy reduces to zero, and kinetic energy gets maximum.
The Kinetic energy at point C is ½ mv2.
Again, v2 = 2gh. Putting the value of v2 in the formula of kinetic energy, we get,
Kinetic energy at C = mgh.
Total energy at C = 0 + mgh= mgh.
The total mechanical energy at points A, B, and C remains the same.
Get Physics Assignments Question Solved by Experts at GoAssignmentHelp!
GoAssignmentHelp has carefully put together a team of physics assignment help experts who are graduates from some of the best Universities and colleges. They are well versed with the latest updates in the world of Physics and will, therefore, be able to give your assignments the best result. The experts ensure that the assignments are original, reliable, and flawless. Each assignment is subjected to multiple revisions and edits. Plagiarism detection tools are used to check for plagiarism, and reliable sources are used to create write-ups. Thus, GoAssignmentHelp, through its professional assignment experts, provides excellent assignment assistance to the students with their Physics assignment needs.






0 responses on "A Guide to the Law of Conservation of Energy"